Sea Trade Routes.
Sea Trade Routes are maritime passages that ocean going vessels use on regular basis in their cargo movement operation around the world. There are eight (8) major Sea Trade Routes in the World. They are listed below:
- North Atlantic Trade Route
- South Atlantic Trade Route
- North Pacific Trade Route
- South Pacific Trade Route
- Oceania Trade Route
- Mediterranean Trade Route
- Indian Ocean Trade Route
- Northern Sea Route (NSR)
The North Atlantic Trade Route links North-eastern United States with North-western Europe. It is the busiest trade route in the world servicing about One-fourth of the world’s foreign trade. This is due to the fact that it connects the two most industrialized regions that are world leaders in manufacturing, trade, finance, transportation and communication.
The greatest volume on this route is transported between the United States and the United Kingdom. A regular exchange of manufactured items is carried out on this route with European countries exporting cars, machinery, steel, chemicals, textiles and food items to the United States and Canada while the North American countries export heavy duty equipment, machinery and wheat to Europe.
The South Atlantic Trade Route connects most of Southern America to the North Atlantic Route. It also services all ocean traffic that passes through the Cape of Good Hope at the southern tip of Africa en-route both North Atlantic and Indian Ocean Trade Routes.
The North Pacific Trade Route The North-Pacific Route which connects the two Americas and eastern Asian coast (with some major important ports in Hawaii) represent one of the major busiest ocean trading routes in the world. It is the second largest trade route by volume.
The South Pacific Trade Route is sea passage that connects the North Pacific trade route to the Southern part of the American continent. In addition, the route services ship traffic through the tip of South America (Tierra del Fuego Archipelago) in southern Chile to the Southern Atlantic Trade Route.
Oceania Trade Route is the trade passage that serves as crossroad for trade traffic between the Northern & Southern Pacific Routes. The bulk of the traffic in this area is facilitated by Australia and New Zealand, the two most industrialized countries in this zone.
Mediterranean Trade Route services all ocean bound traffic between continental Europe, the Middle- and the Far East. The major sea passage on this route is the Suez Canal. It is a major route for all manufactured goods from China en-route Europe and Africa.
Indian Ocean Trade Route is the trade passage that links the Far East to the Middle East, Africa and Europe. With China serving as the manufacturing heart of the world, this route serves as the route for finished products from China to the Middle East, Africa and Europe and the traffic of raw materials from Africa and South America to China. In addition, traffic of energy products such as crude oil and LNG from the Middle East to the rest of the world goes through this route.
Northern Sea Route (NSR) is a shipping route that runs across the Russian Arctic coast from the Kara Sea, through the Siberian coast, and terminating at the Bering Strait. The entire route lies in Arctic waters, within the Russian Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ). The route is made up of two major passages namely the Northeast Passage on the Russian side of the Arctic and the Northwest Passage on the Canadian side.
Global warming has led to rapid melting of Arctic ice caps thus increasing the window of period commercial vessels could travel through this route. The time-frame used to be two months of unrestricted passage. In the end this would serve as a strong alternative to the Suez canal passage.
As the distance through the Northern Sea route from Asia to Europe is considerably shorter than other available sea routes, coupled with the global drive for reduction in CO2 emission, the strategic importance of this route when fully developed is unimaginable. Part of the benefits would be reduction in time at sea which translates into lesser fuel consumption by about half and economies of scale.
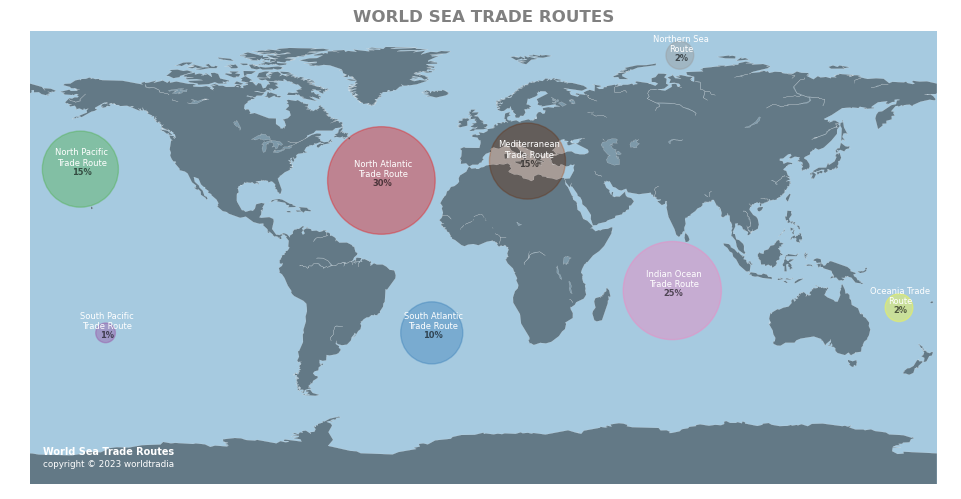
TRADE ROUTES: PERCENTAGE SHARE OF TRAFFIC IN GOODS
- S/N
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- TOTAL
- TRADE_ROUTE
- North_Atlantic
- South_Atlantic
- North_Pacific
- South_Pacific
- Oceania
- Mediterranean
- Indian_Ocean
- Northern_Sea
- TOTAL
- PERCENTAGE_SHARE
- 35
- 30
- 15
- 1
- 2
- 15
- 25
- 2
- 100